The All Electric Society will not only impact the lives of individuals but also fundamentally change the relationships between states and regions. The geopolitical consequences are outlined in a report by the “Global Commission on the Geopolitics of Energy Transformation,” with a title that makes clear the magnitude of these shifts: a new world.
According to the World Energy Transitions Outlook by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewable energy will make up three-quarters of the global energy mix by 2050. Electricity will become the most important energy carrier, covering more than 50 percent of consumption by 2050. This renewable energy-based system will be characterised by a high degree of electrification and efficiency, supplemented by green hydrogen and sustainable biomass.
Profound Implications
These changes in the energy landscape will also lead to significant geopolitical shifts. A report by the “Global Commission on the Geopolitics of Energy Transformation” highlights that the geopolitical and socioeconomic impacts of the new energy age are as profound as the transition from biomass to fossil fuels two centuries ago.
Greater Independence
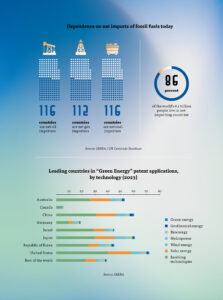
Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are available in some form in most countries and regions around the world. This increases energy security and makes most states less dependent on energy imports. Conflicts over oil and gas will decrease, and the strategic importance of maritime “chokepoints” like the Suez Canal will diminish. The new energy world could also alleviate social, economic, and environmental issues, which are often major causes of geopolitical instability and conflict. However, new dependencies and trade patterns will emerge, such as those created by new renewable energy sources or the closer integration of electricity grids across borders.
New leading Powers
The energy transition will also bring forth new leaders in the energy sector – countries that invest heavily in renewable energy technologies will gain influence on the international stage. For example, China has strengthened its geopolitical position by taking the lead in the race for clean energy, becoming the world’s largest manufacturer, exporter, and installer of solar panels, wind turbines, batteries, and electric vehicles. On the other hand, today’s exporters of fossil fuels will lose their global reach and influence if they do not adapt their economies to the new energy era.
“The renewables revolution enhances the global leadership of China, reduces the influence of fossil fuel exporters and brings energy independence to countries around the world.”
Olafur Grimsson, Chair of the Global Commission on the Geopolitics of Energy Transformation
Access to Energy for more People
Countries that are currently heavily dependent on fossil fuel imports will be able to significantly improve their trade balance in the future by generating a larger share of their energy domestically. This will also reduce the risks associated with vulnerable energy supply lines and volatile fuel prices. Renewable energy will help provide more people with access to energy, create jobs, and promote sustainable economic growth.